
Chain abstraction will drive significant innovations, shaping the future of dapps while addressing many current challenges facing the Web3 ecosystem.
At 2023 year-end, only about 4.2 million unique active wallets were using decentralized applications (dApps) each day.
While this number has grown, the reality is that the Web3 industry still needs to improve two pain points to be in a realistic position to achieve global adoption:
User experience (UX) complexity.
The fragmentation of users and liquidity.
Chain abstraction, a transformative concept being pioneered by projects like Particle Network, is set to solve both issues.
This guide explores the significance of chain abstraction, its benefits, real-world applications, challenges, and future outlook, as well as an in-depth overview of Particle Network’s account-based approach, providing a comprehensive overview of the topic.
The fragmentation of users and liquidity across different blockchains is increasingly an obstacle for Web3 applications.
Chain abstraction refers to the removal of UX frictions typically associated with managing multiple blockchains and distancing end users from front-end blockchain interactions. For example, it allows users to leverage their wallet balances across multiple chains as if they were unified on one.
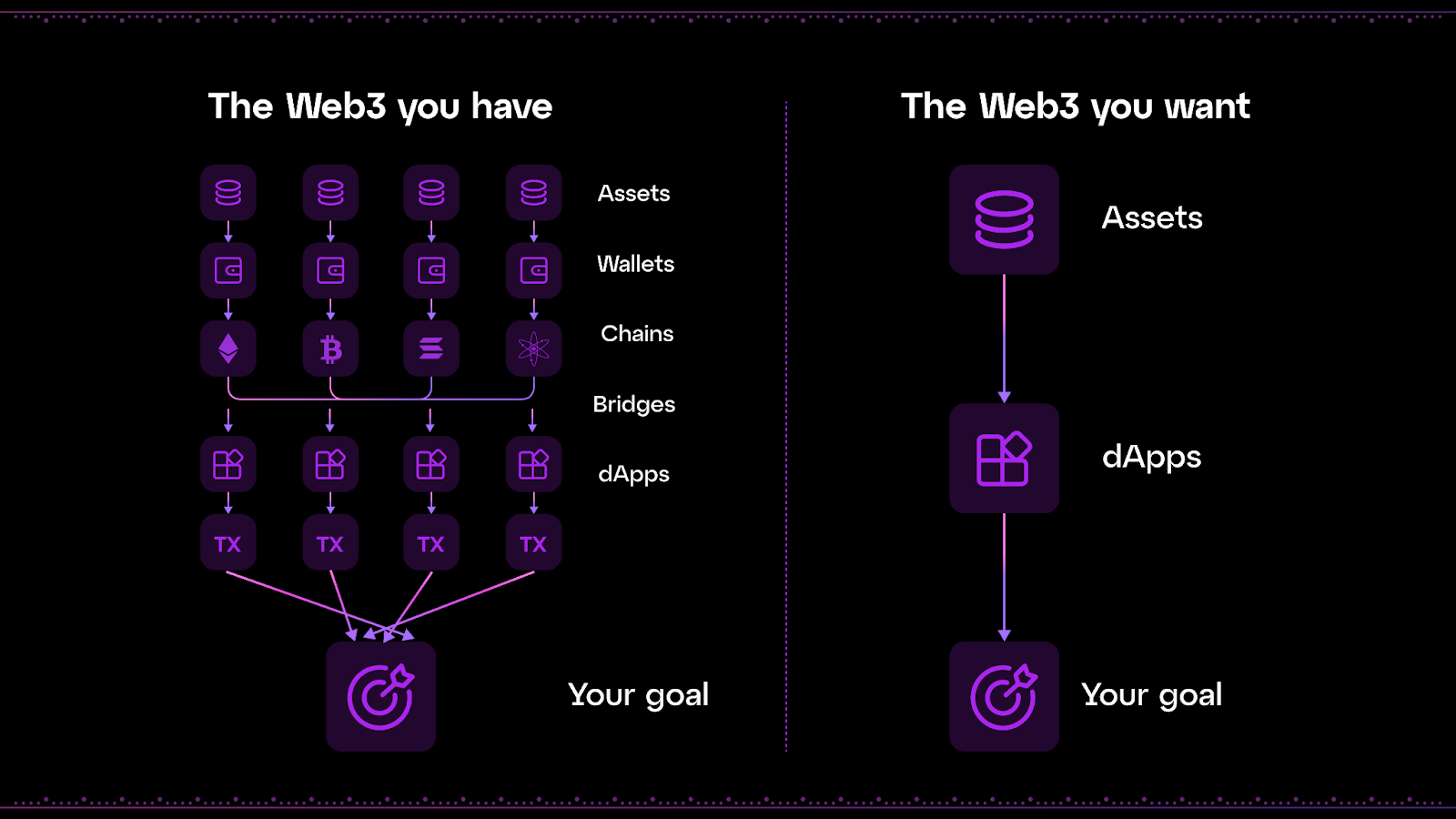
By doing so, chain abstraction empowers the Web3 industry to build applications unbound by the traditional UX confines of individual chains, poised for explosive growth beyond the Web3-native bubble.
Essential to this end result are the several basic benefits that chain abstraction offers. Each enhances the blockchain ecosystem and ultimately shapes chain abstraction’s core value propositions (detailed in the next section) for the Web3 industry:
Chain abstraction allows users to interact across different blockchain networks seamlessly. This focus on interoperability means that assets and accounts can be leveraged uniformly across any blockchain, eliminating the need to manually bridge assets or manage multiple balances, thus reducing friction and increasing efficiency.
Developers can build dApps that are not tied to the liquidity limitations or user base of a specific blockchain, enabling them to tap into resources from across the ecosystem. This flexibility improves network effects and broadens the potential user base for dApps.
Users can interact with dApps without needing to manage balances between chains or understand the underlying blockchain infrastructure used by a given application. Chain abstraction removes the technical complexities away from users, providing a more intuitive and friendly experience.
By enabling dApps to access value and users from around the ecosystem, chain abstraction can help optimize transaction costs and scalability. This is because, in the presence of chain abstraction, developers can choose the most cost-effective and scalable blockchain for specific tasks without regard for their social or economic power.
Bringing the basics of chain abstraction together, we arrive at two pillar value propositions that solve Web3’s prevalent UX and liquidity/user fragmentation issues.
Each of these pillars has widespread application and significant power to transform the Web3 landscape.
Currently, users interacting with dApps across the multi-chain ecosystem are required to manage multiple wallets, balances, and addresses, and remain constantly aware of the technical differences between blockchains. This complexity is a major reason why dApp adoption remains limited worldwide.
From a UX perspective, chain abstraction significantly simplifies Web3 with the elimination of inter-chain barriers. Users can now use applications unhindered; the origin chain of their funds or the base chain of their selected application become background details, largely irrelevant to the user. As a result, users are freed from the longstanding friction and complexity traditionally present when navigating the Web3 landscape.
Chain abstraction decouples blockchain infrastructure from the user experience, enabling seamless interaction with dApps across multiple chains through a single interface. This eliminates the need for users to manage multiple wallets, switch networks, or handle various chain-specific gas fee denominations. For instance, a user can transact across different networks and navigate various dApp experiences without changing wallets or acquiring multiple gas tokens. This level of integration is critical for onboarding billions of users to Web3.
Imagine a scenario where users can perform a range of activities, from buying items to earning rewards, all within a single app, using a unified balance and constant address, without worrying about the underlying blockchain technology.
This vision of a seamless user experience is what chain abstraction aims to achieve.
Fragmentation also hinders dApp development, often forcing developers to choose a blockchain based on its liquidity, co-marketing opportunities, and user access rather than technical needs.
Chain abstraction allows developers to build with the best available technology without feeling forced to choose a single blockchain or a small set of blockchains. Chain abstraction transitions users and liquidity in Web3 from a scarce, ecosystem-bound resource to a global commodity traded between applications.
As Web3 transitions from a monolithic, isolated ecosystem of generalized chains to a modular one with a large volume of specialized chains, the need for chain abstraction grows in prevalence even further. As an industry, Web3 is on the path to ten thousand rollups—developers are beginning to choose to build application-specific blockchains rather than settling for applications built on top of larger, generalized blockchains.
Without chain abstraction, this approach to scaling would introduce significant fragmentation to the ecosystem.
Particle Network shines as a leader at the forefront of advancing chain abstraction, boasting 17 million+ users and 45,000+ developers across their existing products, with building through their L1 notably set to be the next step of the project’s evolution.
By enabling developers to integrate Universal Accounts into their applications, Particle Network allows users from any chain to utilize them, simplifying the complexities associated with cross-chain communication and fostering an integrated, efficient blockchain ecosystem.
This is enabled by the project’s Layer-1 Cosmos blockchain, which acts as a coordination mechanism for accounts on all chains. The Particle Network L1 is intrinsically modular, featuring a high-performance EVM execution environment with built-in access to Cosmos’ Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol for interoperability and rapid cross-chain transaction execution. Serving as a universal settlement layer, Particle Network’s chain abstraction spans both EVM and non-EVM ecosystems.
It’s important to note that chain abstraction is not one problem to solve; it’s many problems grouped. The below image highlights Particle’s unique approach in comparison to other chain abstraction solutions at an economic, integration, and procedural level:
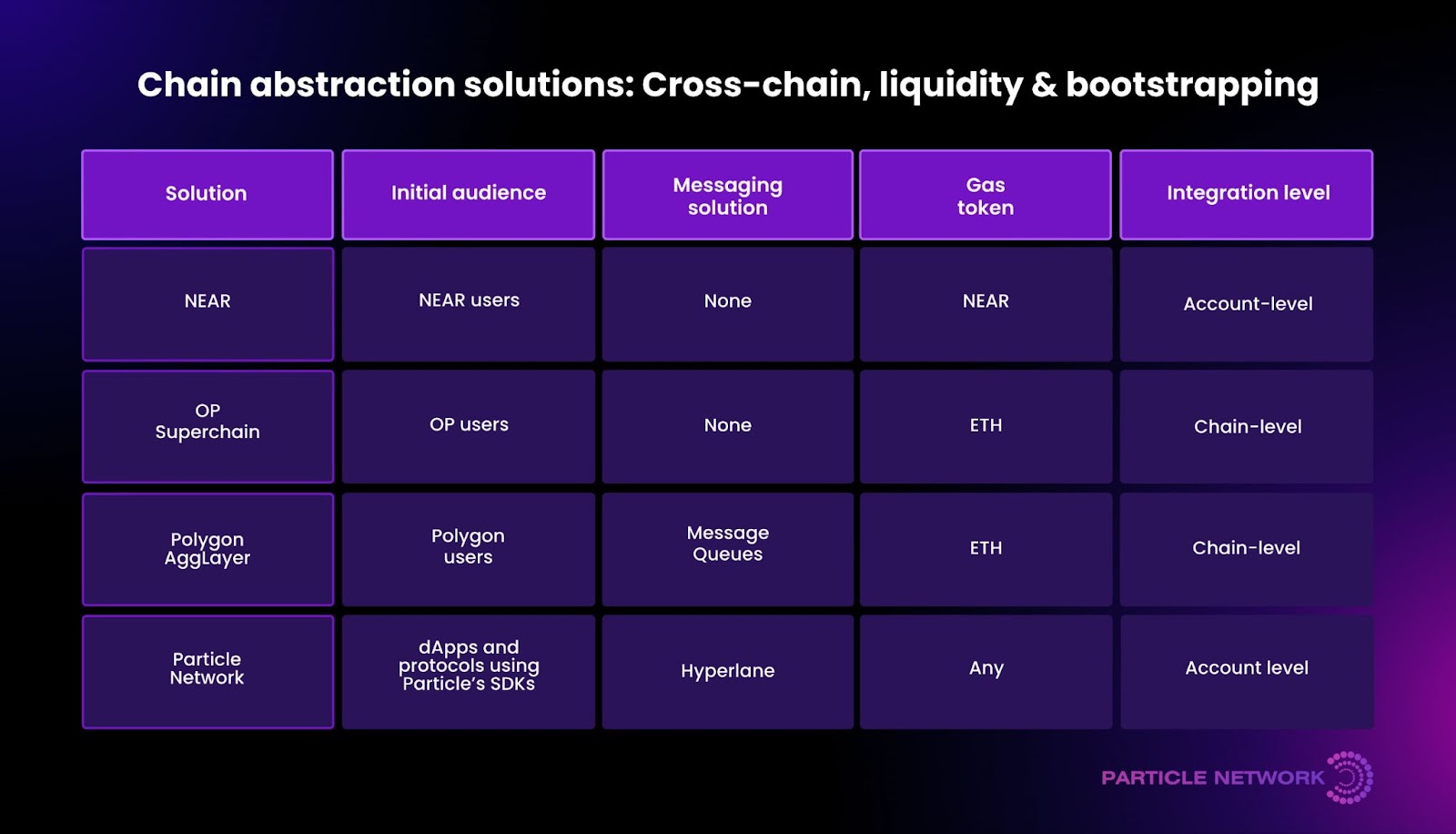
Providing a foundation to its chain abstraction approach, Particle Network offers three core functionalities in its modular L1 that streamline user interactions and transactions across blockchains:
Universal Accounts
Particle Network’s Universal Accounts provide users with a single address and balance across multiple blockchain ecosystems. This simplifies cross-chain wallet management by unifying user interfaces across all chains (EVM and non-EVM).
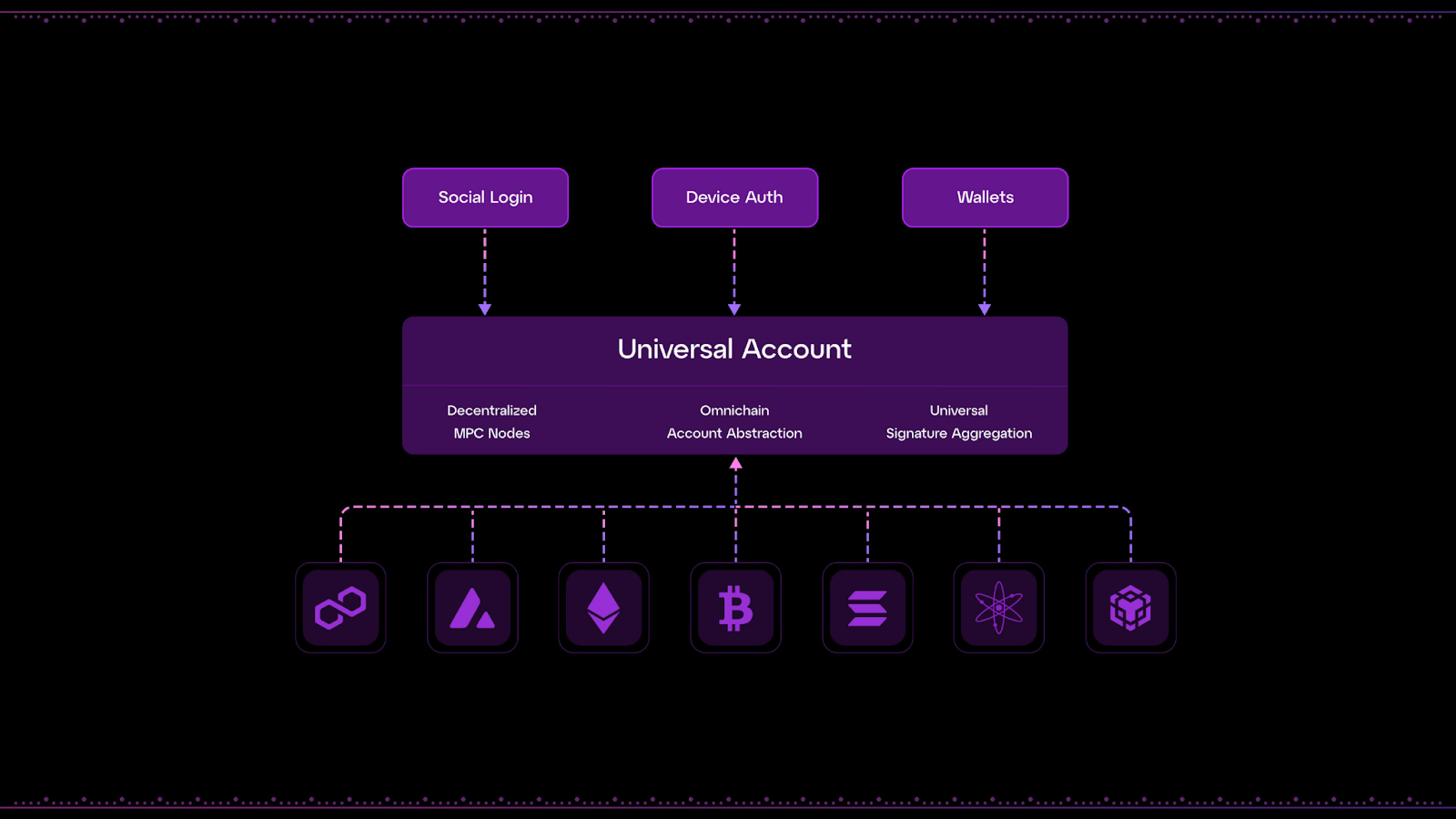
Universal Accounts leverage Universal Liquidity to execute atomic cross-chain transactions, allowing users to deposit and use funds on any blockchain as if they existed on a single chain.
Universal Liquidity unifies the liquidity of different blockchains through the atomic execution of multi-chain transactions. This allows users to interact with new chains without needing to hold tokens on them.
Leveraging universal liquidity, required funds are automatically sourced from users’ balances on other chains, eliminating the need for them to complete the tedious, risky process of manual bridging.
For example, take a scenario in which a user wants to purchase a $300 NFT on an application operating through “Chain D.” This user has $300 in USDT to purchase the NFT, spread equally across three chains: Chain A, Chain B, and Chain C. In such a scenario, Universal Liquidity would perform the following operations:
Another common scenario could involve a user with tokens exclusively on Chain A, but wishing to engage with a DeFi protocol on Chain B. In this case, Particle Network’s Universal Accounts would enable interaction with protocols across any blockchain, eliminating the need to create multiple accounts, manually bridge assets, or hold separate tokens for gas fees.
Universal Gas eliminates the need for multiple chain-specific gas tokens, allowing users to pay for cross-chain transactions with any token. This feature is accessed through Universal Accounts, enabling users to pay gas fees with tokens from any source chain, such as paying fees on Arbitrum using USDT from Base.
The future of chain abstraction looks promising, addressing the critical pain points of UX complexity and the fragmentation of users and liquidity. As the technology evolves, chain abstraction will drive significant innovations, shaping the future of dApps while addressing many current challenges facing the Web3 ecosystem.
Through the proliferation of chain abstraction led by pioneers like Particle Network, the Web3 industry can achieve seamless, user-friendly experiences and ultimately attract a global audience.
To learn more about chain abstraction and stay up to date on Particle Network’s progress, head to their website and follow them on X.
Source: blockworks.co